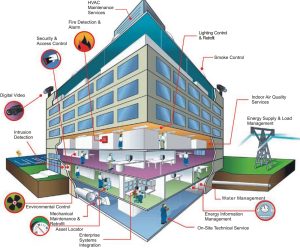
 A Building Management System (BMS), also known as a Building Automation System (BAS), is a centralized and integrated system that monitors, controls, and manages various building systems and equipment to optimize their performance, enhance occupant comfort, and improve energy efficiency. BMS technology is commonly used in commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and large residential complexes to streamline operations and provide real-time insights into building functions.
A Building Management System (BMS), also known as a Building Automation System (BAS), is a centralized and integrated system that monitors, controls, and manages various building systems and equipment to optimize their performance, enhance occupant comfort, and improve energy efficiency. BMS technology is commonly used in commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and large residential complexes to streamline operations and provide real-time insights into building functions.
Key components and features of a Building Management System include:
Sensors and Monitoring Devices: BMS incorporates a network of sensors and monitoring devices to gather data on various building parameters such as temperature, humidity, occupancy, lighting levels, air quality, and energy consumption.
Centralized Control: The heart of the BMS is the central control unit or software platform that enables users to monitor and control building systems from a single interface. This allows facility managers to adjust settings, set schedules, and respond to alarms.
HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning): BMS controls HVAC systems to maintain optimal indoor comfort and air quality. It can adjust temperature, humidity, and air circulation based on occupancy and external conditions.
Lighting Control: BMS manages lighting systems by dimming or turning off lights in unoccupied areas, optimizing natural light use, and adjusting lighting levels to reduce energy consumption.
Energy Management: BMS helps optimize energy usage by monitoring energy consumption, identifying energy inefficiencies, and implementing energy-saving strategies such as load shedding, peak demand management, and optimizing equipment schedules.
Security and Access Control: BMS integrates security systems such as access control, intrusion detection, and surveillance cameras to enhance building security and manage access to different areas.
Fire Detection and Suppression: BMS can monitor fire detection systems and control fire suppression systems, helping to quickly respond to fire emergencies and minimize damage.
Elevators and Escalators: BMS can manage elevator and escalator systems, optimizing their operation and energy use based on traffic patterns.
Water Management: BMS can monitor and control water supply, distribution, and sewage systems to ensure efficient water usage and address leaks or issues.
Remote Monitoring and Control: Some BMS platforms offer remote access, allowing facility managers to monitor and control building systems from off-site locations through web-based interfaces or mobile apps.
Alerts and Alarms: BMS generates alerts and alarms for abnormal conditions, malfunctions, or potential issues, enabling prompt responses and preventive maintenance.
Data Analytics and Reporting: BMS collects and analyzes data to provide insights into building performance, energy consumption patterns, and opportunities for optimization. Reports and dashboards help facility managers make informed decisions.
Benefits of a Building Management System:
Energy Efficiency: BMS helps reduce energy consumption by optimizing systems and equipment based on real-time data and occupancy patterns.
Cost Savings: Improved energy efficiency and reduced maintenance costs lead to overall cost savings.
Occupant Comfort: BMS ensures consistent indoor comfort and air quality by controlling HVAC and lighting systems.
Remote Management: Remote access allows facility managers to monitor and control systems from anywhere, improving efficiency.
Sustainability: BMS contributes to sustainable building practices by reducing resource usage and environmental impact.
Maintenance Optimization: BMS enables predictive maintenance by identifying equipment issues before they lead to failures.
Building Management Systems play a crucial role in modern building operations, offering automation, control, and optimization to create efficient, comfortable, and sustainable environments.