 FIDIC stands for the “International Federation of Consulting Engineers,” an international organization that produces standard forms of contracts for the construction and engineering industry. These contracts are widely used as the basis for agreements between various parties involved in construction and infrastructure projects, including clients, consultants, contractors, and sub-contractors. FIDIC contracts are designed to provide a fair and balanced framework for managing project risks, responsibilities, and obligations.
FIDIC stands for the “International Federation of Consulting Engineers,” an international organization that produces standard forms of contracts for the construction and engineering industry. These contracts are widely used as the basis for agreements between various parties involved in construction and infrastructure projects, including clients, consultants, contractors, and sub-contractors. FIDIC contracts are designed to provide a fair and balanced framework for managing project risks, responsibilities, and obligations.
Key features and components of FIDIC contracts include:
- Standardization: FIDIC contracts offer standardized templates that outline the roles, responsibilities, and obligations of each party involved in a construction project. They provide a consistent framework that is recognized and understood globally.
- Roles and Responsibilities: FIDIC contracts define the roles and responsibilities of the client, consultant, and contractor. They specify who is responsible for design, construction, quality control, approvals, and various project-related activities.
- Risk Allocation: FIDIC contracts allocate various project risks between the parties, aiming to achieve a balanced distribution of risks and liabilities. This helps prevent disputes and ensures that each party is accountable for the risks they are best equipped to manage.
- Payment Terms: FIDIC contracts outline the payment terms, including the schedule of payments, invoicing procedures, and provisions for variations (changes) to the scope of work.
- Variations and Changes: FIDIC contracts include provisions for dealing with changes to the scope of work, allowing for adjustments to the project based on unforeseen circumstances or evolving project requirements.
- Dispute Resolution: FIDIC contracts typically provide mechanisms for resolving disputes that may arise during the course of the project. This often includes procedures for negotiation, mediation, and arbitration.
- Time Management: FIDIC contracts address project scheduling, deadlines, and extensions of time, helping manage project timelines and potential delays.
- Quality and Performance: The contracts outline requirements for quality control, testing, and performance standards to ensure that the project meets the specified requirements.
- Termination and Suspension: FIDIC contracts include provisions for the termination or suspension of the contract under certain circumstances, such as non-performance or insolvency of a party.
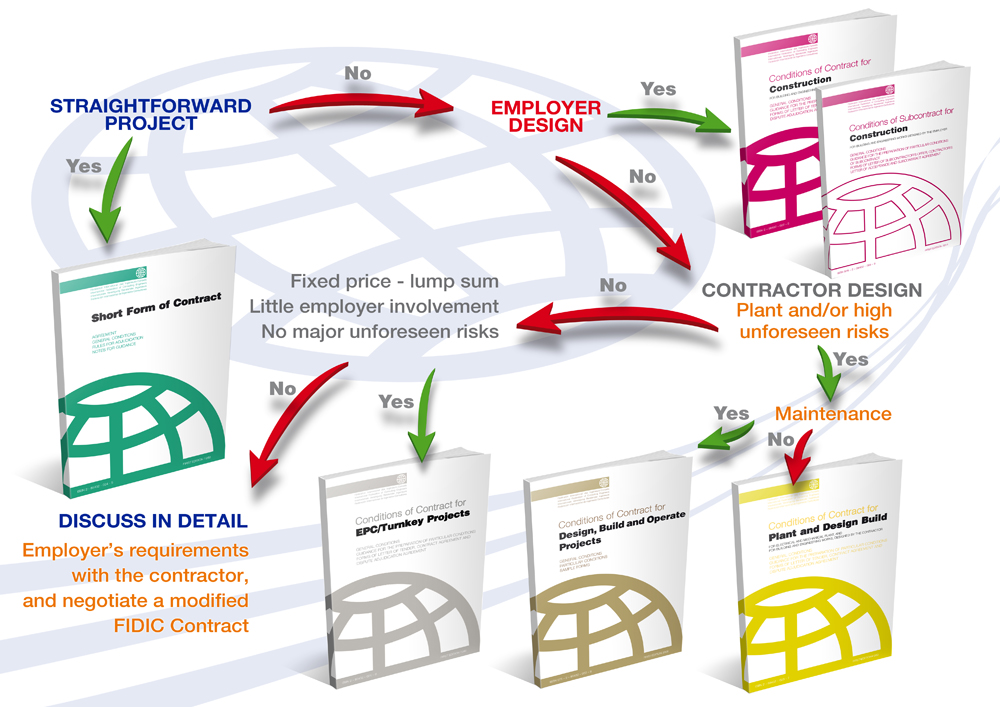
FIDIC contracts come in different forms, each tailored to specific types of projects and contractual arrangements. Some of the commonly used FIDIC contract forms include:
- FIDIC Red Book: Conditions of Contract for Construction (For Building and Engineering Works Designed by the Employer)
- FIDIC Yellow Book: Conditions of Contract for Plant and Design-Build (For Electrical and Mechanical Plant, and for Building and Engineering Works, Designed by the Contractor)
- FIDIC Silver Book: Conditions of Contract for EPC/Turnkey Projects (Engineering, Procurement, and Construction)
- FIDIC Green Book: Conditions of Contract for Short Form of Contract (For smaller and less complex projects)
It’s important to note that while FIDIC contracts provide a comprehensive framework, parties should still engage legal and contractual experts to adapt the contracts to the specific requirements and laws of their jurisdictions and projects. Additionally, FIDIC contracts have undergone revisions over the years, so it’s advisable to use the latest version available and consult the official FIDIC publications for accurate and up-to-date information.
